Solu-Medrol: Friend or foe?
2 Comments
/
Acute spinal cord injury (SCI) secondary to external trauma or intervertebral disk disease is a common cause for paresis and ataxia in people and dogs. This article discusses the pros and cons of Solu-Medrol and reviews the veterinary and human medical literature.
Diagnosis and treatment of glaucoma
Ruth Marrion, DVM, PhD, DACVO
Bulger Veterinary Hospital, North…

Injury prevention and the canine athlete
The number of dogs and owners involved in canine sports in the United States has grown exponentially in recent years. The American Kennel Club reports that, in 2011 alone, there were one million entries for agility trials and 22,000 athletic events. This review article provides important tips on injury prevention in the canine athlete.

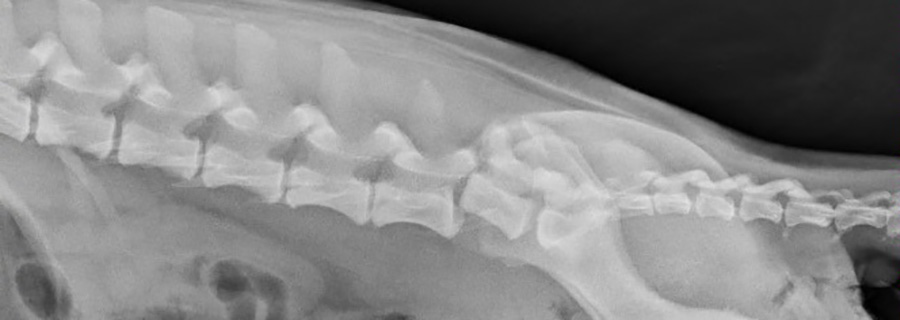
Seeing between the lines
A 4-month-old female Labrador Retriever is presented for progressive lethargy and decreased appetite of 10 days duration. Her owners report that she vocalized while trying to stand this morning, and then would not get up. Review the radiographs. What's your radiographic diagnosis?
Interventional analgesia: Part II
As veterinary pain management becomes more like human pain management in offering patients a broader range of strategies for the treatment of acute and chronic pain, the interventional strategies and the techniques described below will become more commonplace.
Interventional analgesia, part I
Interventional pain management in animals is an application of image-guided procedures which benefit veterinary patients with both acute and chronic pain. This 2-part series provides an overview of interventional analgesia in animals.

Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence is defined as loss of voluntary control of urination, resulting in leakage of urine from the urinary system to the exterior of the body. While UI has consequences for our clients’ homes, it can also cause significant pathology to our patients. Timely diagnosis and control of this potentially chronic problem will help to ameliorate these concerns.
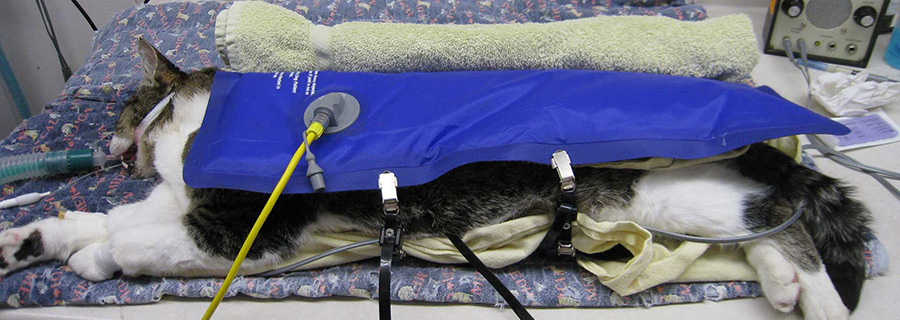
Perioperative hypothermia
Body temperature is closely maintained in mammals around an optimal set point at which ideal cellular function can occur. This is a complex process that ultimately results in a balance between heat production and heat loss. The hypothalamus acts as the main regulator of this process with multiple sensors throughout the body.
