
Medical evaluation of congenital hepatic disease in dogs
The two most common types of congenital hepatic disease include portosystemic vascular anomalies (PSVA) and microvascular dysplasia (MVD, now technically termed portal vein hypoplasia without a macroscopic anomaly). The clinical course and treatment options differ depending on the underlying disease, and an accurate diagnosis is essential for future management and prognosis.
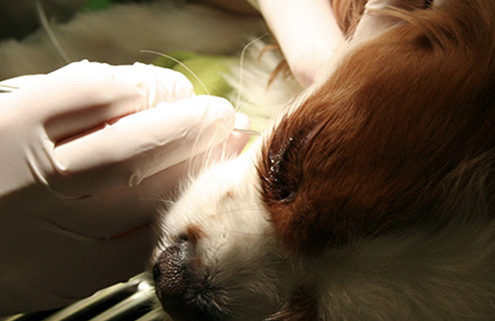
Dental radiography: A fresh look
Intraoral radiology is an essential tool in the diagnosis and treatment of dental problems. It is perhaps the tool that separates mere “cleaning and pulling” from more comprehensive veterinary dentistry.
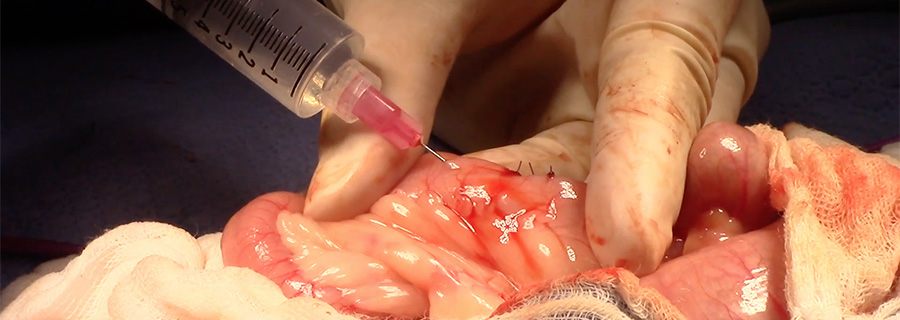
Intestinal leak testing following enterotomy
An important task during enterotomy surgery is testing for leaks following intestinal closure. The instructional video below demonstrates intestinal leak testing with and without instruments.

Laryngeal paralysis: The inspiration and the aspiration
Laryngeal paralysis is one of the more common upper respiratory emergencies seen in our aging canine population. It is frequently diagnosed in the spring to summer time as the weather begins to warm and we are more active with our canine companions.

The yellow fellow: Evaluation of the icteric cat
Icterus is the presence of yellow discoloration of non-pigmented body surfaces (i.e. mucous membranes, sclera, skin) or plasma, and this results from an accumulation of bilirubin in the blood stream.
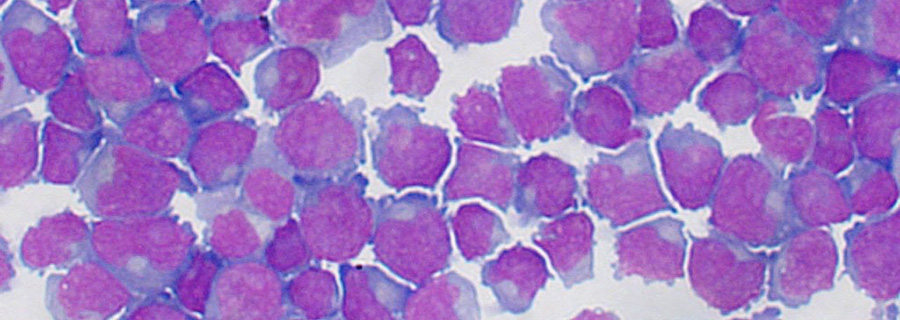
Canine lymphoma
Lymphoma is one of the most commonly encountered canine cancers, and it is seen frequently in clinical practice. Lymphoma arises from neoplastic lymphocytes. Typically it is first recognized in lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, liver, spleen, bone marrow); however, it can be seen in any location in the body.
