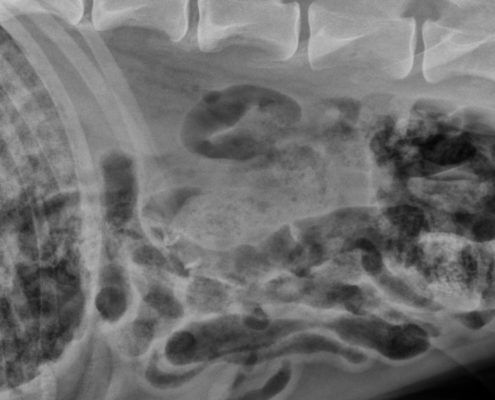
Imaging the acute abdomen
The term acute abdomen refers to a patient presenting with acute clinical signs and abdominal pain due to a disease process of an abdominal structure. Read more about this common presentation in emergency veterinary medicine.
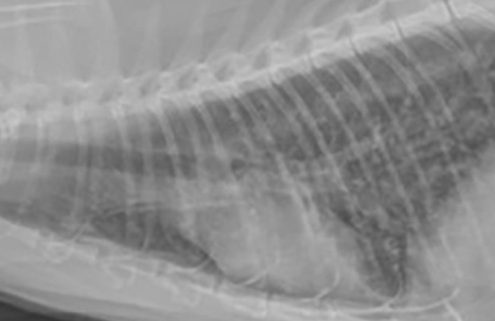
Imaging diagnosis of common gastrointestinal and respiratory emergencies
Interpretation of radiographs, or any additional diagnostic imaging studies, should be performed in a systematic manner to ensure evaluation of all structures and consideration of all possible diagnoses.
Making the most of your ultrasound machine
This post describes how to manipulate user controls to obtain better ultrasound images in veterinary medicine.

Feline head imaging: Continuity with practitioner and radiology
Diseases of the head are often initially imaged with radiographs in the clinic. This article discusses the basics of feline head radiographic imaging.
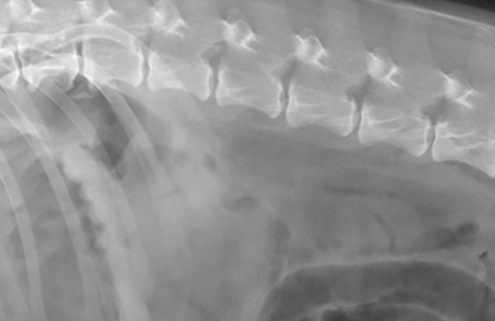
Radiography vs. ultrasound in the dog with acute abdominal signs
In the emergency setting, the primary goal of diagnostic imaging is to help differentiate surgical from non-surgical conditions. The benefits and limitations of survey radiography and abdominal ultrasound are discussed in this post.
Tips for digital & teleradiology
With more and more veterinary practices transitioning to digital radiography, teleradiology consultations are on the rise. Ease of digital image transmission/submission, and quick turn-around times have greatly facilitated this trend in veterinary medicine. This article provides some tricks and tips that will help you get the most out of your teleradiology interpretations with fewer calls, emails, and repeat radiographs to follow up your interpretations.

What’s your radiographic diagnosis? Lame Maine Coon
What is your radiographic diagnosis for this 2-year-old castrated male Maine Coon cat that was presented to the emergency department for evaluation following an acute onset of left hind limb lameness after being spooked and running away from a vacuum cleaner?
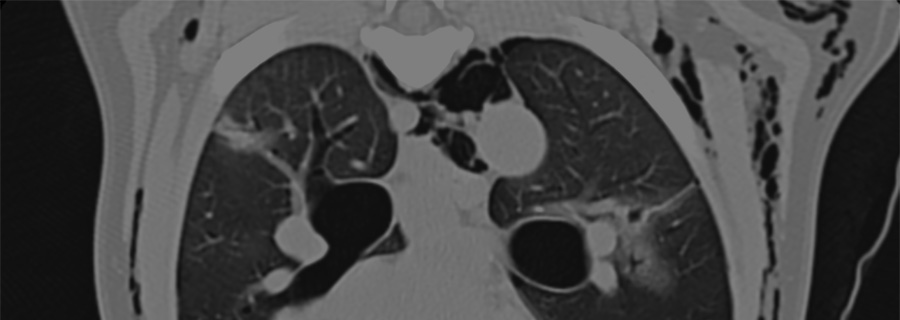
Thoracic CT: More than just a pretty picture
Computed tomography (CT) is routinely used in human medicine to examine pulmonary, tracheobronchial and mediastinal abnormalities, and is the standard screening test for pulmonary metastasis. CT is more sensitive and accurate than radiography for detecting interstitial disease and pulmonary nodules even in the presence of pleural effusion. This article discusses thoracic CT in veterinary patients.

What's your radiographic diagnosis? Respiratory arrest during dental cleaning
Jennifer O. Brisson, DVM, DACVR
Massachusetts Veterinary Referral…

Seeing between the lines
1 Comment
/
A 4-month-old female Labrador Retriever is presented for progressive lethargy and decreased appetite of 10 days duration. Her owners report that she vocalized while trying to stand this morning, and then would not get up. Review the radiographs. What's your radiographic diagnosis?
Portosystemic shunts
Portosystemic shunts are the most common hepatobiliary congenital abnormality diagnosed in veterinary medicine. When a portosystemic shunt is present, the portal circulation enters directly into the systemic circulation...

Imaging diagnosis: Coughing German Shepherd
A German Shepherd dog was referred for evaluation of gagging and labored breathing of two weeks duration. View the radiographs. What's your radiographic diagnosis?

What's your radiographic diagnosis? Vomiting Bulldog
A 6-month-old, sexually-intact male English Bulldog was presented to the ER Department for acute onset vomiting for approximately six hours. What is your radiographic diagnosis?
